Where and how is social status processed in the brain?
When viewer monkeys watched videos of pairwise dominant/subordinate interactions, they showed a looking preference for the dominant individuals. Longer looking at dominant individuals may indicate an understanding of the hierarchical relationship between the interacting individuals. Alternatively, the viewer monkeys may have only learned the reputation of each individual (the likelihood of being aggressive or appeasing). We are currently carrying out control experiments to discriminate between these alternative explanations.
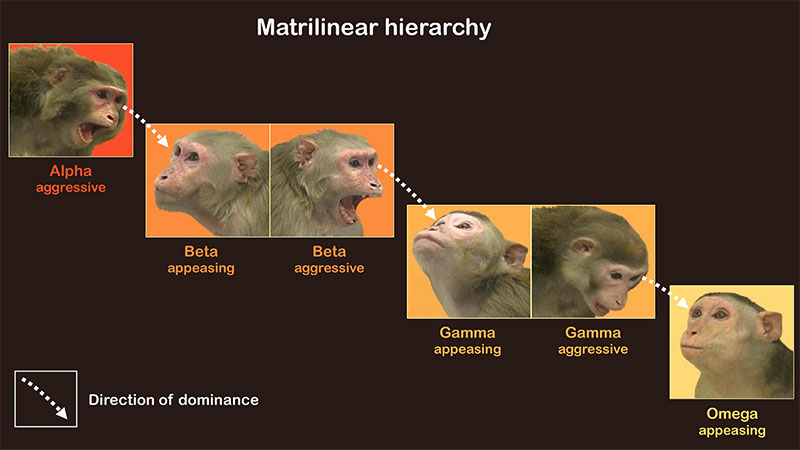
The future steps in completing the goals of this project are outline below.
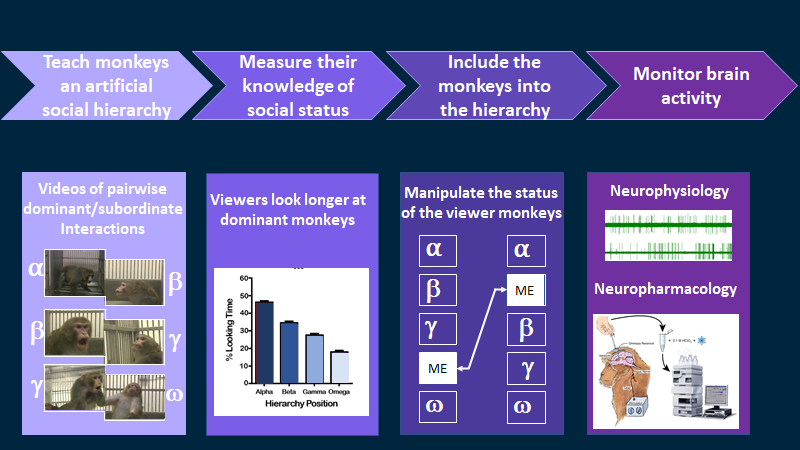
The ultimate goal of this project is to understand where and how social status is represented in the brain and how rising or falling in a hierarchy alters the neurochemistry of the brain.